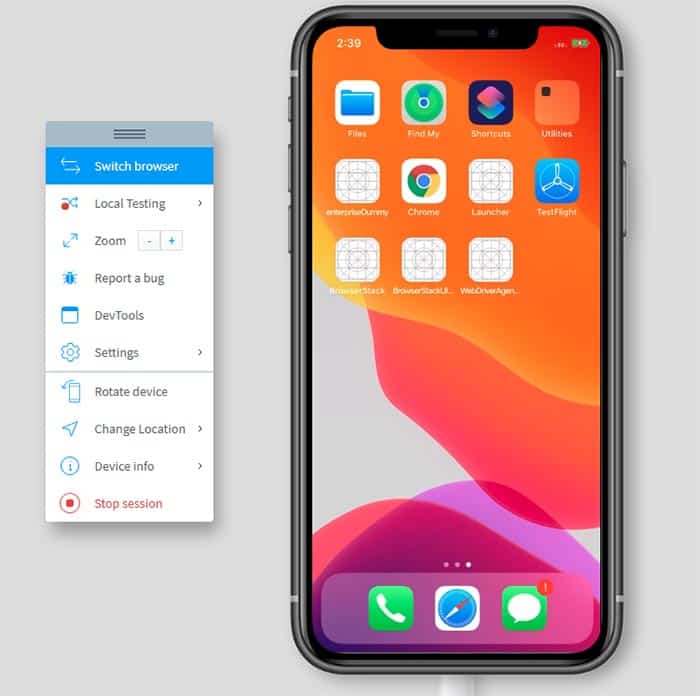
- Simulate Ios App On Mac
- Emulate Ios App On Mac Free
- Iphone Simulator Mac
- Iphone Emulator For Macbook
- Can You Emulate On Ios
7 Best iOS Emulators for MAC in 2020
Using an iOS emulator to run a iOS App on other operating system has many advantages. So, here are the Best iOS Emulators for Windows (2019). App.io is currently counted as one of the best iOS emulators for Windows 7/8/8.1/10 and Mac PC. App.io is the top alternative to appetize.io. So if you are facing issues with appetize then consider using this emulator out. Hello Guys:D How cool is it to emulate iPhone and Android in your browser it self:D Just upload the apk for Android or.zip apps for iPhone.
Do you want to run iOS applications on MAC? This can be done using iOS Emulators. If you don’t own an iPhone but want to try an interesting application available only for iOS then you can use iOS Emulators to run that app on you MAC. Before knowing more about iOS Emulators, let me tell you about emulators. Emulators are a great way to strike out in the world of iOS. Generally, an emulator refers to a hardware or software that enables one system to operate or behave like another system. Emulators can be used for MAC. Emulators are an imperative tool for developers. They help the developers to know how their app will look and behave or respond. These are the programs that help to create a virtual iOS on the operating system to run a particular program. It’s important to note that emulators only create a virtual environment for software but the hardware remains the same. Sometimes it may happen that various apps require a specifichardware; such apps may not work properly. For example, if an application requires touch feature and your MAC doesn’t have it, then that particular app will not work on your MAC. Emulators also need a good quality RAM (minimum 4 GB RAM). One must keep in mind that more the RAM is smoother will the emulator work. An iOS Emulator refers to the software that runs on MAC and allows the users to create a virtual environment for mobile operating systems. By using an iOS Emulator, the user can install and run all the apps and games as can be done on an iPhone. App or game developers use iOS Emulators to properly scale or test their applications. Various iOS Emulators for MAC available in the market are listed below.
- Smartface Smartface is an iOS Emulator which is mostly used by app developers. App developers use it to test their apps for various iPhones and iPads. The emulator is paid and starts at $99. It also avails the users with a free version to test it. It is an ideal emulator for testing cross-platform iOS apps. It also functions as an Android and iOS debugger.
-iPadian iPadian is yet another unanimous iPhone emulator that offer a UI similar to iOS. It costs around $20 and requires Adobe Air for proper functioning. It consumes low resources and can be used to play dozens of iOS games and run various iOS apps. It is not a full-fledged emulator. It provides the user with the list of apps that he/she can induce on the desktop to see how it will appear on iPad. It is user friendly, smooth and clutter-free. It has been a choice of professionals for long and comes with a customizable interface and includes a facebook notification widget as well. One thing to note is that it does not allow access to the official Appstore. The user can run the apps specifically designed for iPadian simulator.
Simulate Ios App On Mac
- Appetize.io Appetize.io is a powerful emulator and an alternative to App.io. It is used for developing and testing iOS apps. It is a cloud-based iOS emulator and eliminates the need for downloading additional software. A user can use Appetize.io completely free for about 100 minutes per month. After exceeding the limit of 100 min/month, the user will be charged $0.05 per minute.Appetize.io runs iOS and Android apps within a web browser on any computer. It has an easy access to network traffic, debug logs and video recordings. It closely resembles an iPhone which helpthe users to easily develop, test and update the apps.
-Air iPhone This iOS emulator has a UI that resembles iOS 6 and can be used for playing games and using iOS applications. This iOS Emulator requires anAdobe AIR framework to work correctly. Developers use this emulator for testing the layout before finally compiling the application. It is Simple and has an intuitive UI.
- iPhone Stimulator This software allows users to use and interact with iOS apps and games. The UI of this simulator is identical to that of original iOS, but the UX is different. Consequently, it’s a simulator and not an emulator. You can use this iOS simulator for playing iOS games. iPhone Simulator offers a realistic simulation. It also enables access to the clock, calculator, notepad and iOS system preferences. iPhone Simulator is mainly used for games and other smaller apps, due to the lack of cutting-edge features. The lack of bugs in the emulation is also impressive and helps deliver a near-native iPhone gaming experience. Another additional benefit is that it’s free.
- Ripple Emulator Ripple emulator helps you emulate an iPad on PC for testing purposes and is an easy option since it is not software-based, requiring a Google Chrome extension. It can be used for developing and testing apps while online on your PC. However, there is a drawback of Ripple; it is still in the beta stage presently. You are likely to encounter bugs. Ripple Emulator is available as a browser extension. So, you can install it in your Chrome browser and setup everything easily. Overall, it works fine and you can test or run iOS apps and games. While Appetize.io is a browser-based iPhone emulator for PCs, Ripple does its job in the form of a Chrome extension. It’s popular for testing cross-platform mobile and HTML5 applications without going through a complicated setup process. Targeted towards platforms like PhoneGap and Webworks, Ripple aims to help developers by providing features like HTML DOM Inspection, Automated Testing, JS Debugging, and more. In real-time, one can run the apps on different screen resolutions and devices. This iOS emulator for your computer doesn’t need to be restarted if you choose a new device, which makes the experience pretty convenient.
- Xamarin TestFlight Emulator Xamarin TestFlight is the next iPhone emulator. It is the official Apple emulator that is created for testing the apps developed for iOS. It is worth noting, that Xamarin TestFlight is not meant for beginners, there’s some learning curve to use this emulator to its full potential. You can upload your app and check its compatibility on different iOS devices.Furthermore, Xamarin TestFlight can only run applications that are developed for iOS 8 or later. These were all the best iOS Emulators for MAC. User can choose from the above according to their needs and satisfaction. Most of emulators are focused on app development and testing but some are also based on playing games and running various iOS apps. Depending on the need, the user can choose any of these emulators.
General information
What is Basilisk II?
Basilisk II is an Open Source 68k Macintosh emulator. That is, it allows you to run 68k MacOS software on your computer, even if you are using a different operating system. However, you still need a copy of MacOS and a Macintosh ROM image to use Basilisk II. Basilisk II is distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Xamarin TestFlight is an iOS emulator that lets you run iOS apps on Windows PC and also lets you airplay iPhone to Mac as well. And it runs on both really well! For the moment the app is owned by Apple, so, it is very reliable. Unfortunately, it is not a free app and the installation is also a bit complicated but the performance is great. Once the iPad boots in ARM mode, iTunes launches the Mavericks installer on the Mac, and makes the iPad available as a destination disk. The installation process is the same as it would be on a Mac, and when it’s done, your iPad will boot into Mac OS X and work just like a tiny Mac.
For more information, see the README file. If you are interested in learning how Basilisk II works internally, there is a Technical Manual available (knowledge about programming and computer architecture is required).
Available ports
Basilisk II has been ported to the following systems:- Unix with X11 (Linux i386/x86_64, Solaris 2.5, FreeBSD 3.x, IRIX 6.5)
- Mac OS X (PowerPC and Intel)
- Windows NT/2000/XP
- BeOS R4 (PowerPC and Intel)
- AmigaOS 3.x
Some features of Basilisk II
- Emulates either a Mac Classic (which runs MacOS 0.x thru 7.5) or a Mac II series machine (which runs MacOS 7.x, 8.0 and 8.1), depending on the ROM being used
- Color video display
- CD quality sound output
- Floppy disk driver (only 1.44MB disks supported)
- Driver for HFS partitions and hardfiles
- CD-ROM driver with basic audio functions
- Easy file exchange with the host OS via a 'Host Directory Tree' icon on the Mac desktop
- Ethernet driver
- Serial drivers
- SCSI Manager (old-style) emulation
- Emulates extended ADB keyboard and 3-button mouse
- Uses UAE 68k emulation or (under AmigaOS and NetBSD/m68k) real 68k processor
Important:The information in this document is deprecated in Xcode 9. For Xcode 9 and later, see Simulator Help by choosing Help > Simulator Help in Simulator.
Simulator app, available within Xcode, presents the iPhone, iPad, or Apple Watch user interface in a window on your Mac computer. You interact with Simulator by using the keyboard and the mouse to emulate taps, device rotation, and other user actions.
The chapter presents the basics of using Simulator. You can perform these steps using your own iOS app or, if you do not have an app to use, with the HelloWorld sample code. For more detailed information on interacting with Simulator and using it to test and debug your apps, refer to the later chapters in this guide.
Access Simulator from Xcode
There are two different ways to access Simulator through Xcode. The first way is to run your app in Simulator, and the second way is to launch Simulator without running an app.
Running Your iOS App
When testing an app in Simulator, it is easiest to launch and run your app in Simulator directly from your Xcode project. To run your app in Simulator, choose an iOS simulator—for example, iPhone 6 Plus, iPad Air, or iPhone 6 + Apple Watch - 38mm—from the Xcode scheme pop-up menu, and click Run. Xcode builds your project and then launches the most recent version of your app running in Simulator on your Mac screen, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Note: If you are testing an app with a deployment target of iPad, you can test only on a simulated iPad. If you are testing an app with a deployment target of iPhone or universal, you can test on either a simulated iPhone or a simulated iPad.
Running Your watchOS App
To run your WatckKit app, choose a combination of an iOS device and watchOS device from the Xcode scheme pop-up menu. For example, to run the watch app in a 38mm watch paired with an iPhone 6, choose 'iPhone 6 + Apple Watch - 38mm' from the scheme pop-up menu.
Running the WatchKit target launches two simulators, one for the iOS device and one for the watchOS device. Figure 1-2 shows an iPhone 6 and a 42mm watch running in two different simulators.
Running Your tvOS App
To run your tvOS App, choose a tvOS device from the Xcode scheme pop-up menu. Running the tvOS target launches the most recent version of your app in a simulated new Apple TV device, as shown in Figure 1-3.
Launching Simulator Without Running an App
At times, you may want to launch Simulator without running an app. This approach is helpful if you want to test how your app launches from the Home screen of a device or if you want to test a web app in Safari on a simulated iOS device.
To launch a Simulator without running an app
Launch Xcode.
Team viewer download per mac. Do one of the following:
Choose Xcode > Open Developer Tool > Simulator.
Control-click the Xcode icon in the Dock, and from the shortcut menu, choose Open Developer Tool > Simulator.
To launch a watchOS Simulator without running an app
Launch Xcode.
Do one of the following:
Choose Xcode > Open Developer Tool > Simulator (watchOS).
Control-click the Xcode icon in the Dock, and from the shortcut menu, choose Open Developer Tool > Simulator (watchOS).
Simulator opens and displays the Home screen of whichever simulated device was last used.
View the Installed Apps
From the Home screen, you have access to all of the apps that are installed in the simulation environment. There are two ways to access the Home screen in Simulator from your app:
Press Command-Shift-H.
Choose Hardware > Home.
Use the installed apps to test your app’s interaction with them. For example, if you are testing a game, you can use Simulator to ensure that the game is using Game Center correctly.
iOS Device Home Screen
Much like the Home screen on an iOS device, the simulator’s iOS Home screen has multiple pages. After clicking the Home button (or accessing the Home screen through the Hardware menu), you arrive at the second page of the Home screen. To get to the first page, where all of the preinstalled apps are found, swipe to the first Home screen by dragging to the right on the simulator screen.
On the Home screen, you see that all of the apps that have been preloaded into Simulator. See iOS Device Home Screen.
The apps that you see on the Home screen are specific to the iOS device simulation environment. Because Passbook and the Health app are available only for the iPhone, these apps don’t appear if you are simulating a legacy device or an unsupported device type.
watchOS Device Home Screen
The Home screen for a simulated watchOS device behaves the same as it would on an actual device. You can click and drag to simulate the finger dragging around the screen and launch an app by clicking on it. Figure 1-4 shows the home screen of a 42mm watch with a developer app, the Lister sample code.
Use Safari to Test Web Apps
From the Home screen, you can access Safari within Simulator. Use Safari to test your iOS web apps directly on your Mac.
From the Home screen, click Safari.
In the address field in Safari, type the URL of your web app and press the Return key.
If your Mac is connected to the Internet, it displays the mobile version of the URL you specified. For example, type apple.com into the address field and press Return. Safari displays the Apple website. See Figure 1-6.
Use Maps to Simulate Location Awareness
Simulator provides tools to assist you in debugging your apps. One of the many features you can debug in Simulator is location awareness within your app. Set a location by choosing Debug > Location > location of choice. The menu has items to simulate a static location or following a route.
A simulated watchOS device with the location set to None checks the paired iPhone device for the location.
You can specify your own location, which can be seen in the Maps app.
From the Home screen, click Maps.
Choose Debug > Location > Custom Location.
In the window that appears, type the number
40.75in the latitude field and the number-73.75in the longitude field.Click OK.
Click the Current Location button in the bottom-left corner of the simulated device screen.
After completing this task, notice that the blue dot representing your location is in New York, NY, near the Long Island Expressway, as shown in Figure 1-7.
Change the Simulated Device and OS Version
Simulator provides the ability to simulate many different combinations of device type and OS version. A device type is a model of iPhone, iPad, or Apple TV. Some iPhone devices can also have a paired Apple Watch. Each device-OS combination has its own simulation environment with its own settings and apps. Simulator provides simulators for common device-iOS, device-watchOS-iOS device, and device-tvOS combinations. You can also add simulators for a specific combination you want to test. However, not all device type and OS version combinations are available.
Note: To test apps for the iPad mini, use a simulated iPad with the same pixel resolution as the iPad mini.
You can switch between different device-OS combinations. Switching closes the window for the existing device and then opens a new window with the selected device. The existing device goes through a normal OS shutdown sequence, though the timeout might be longer than the one on a real device. The new device goes through a normal OS startup sequence.
To change the simulated device
Choose a Hardware > Device > device of choice.
Simulator closes the active device window and opens a new window with the selected device.
If the device type and OS version combination you want to use is not in the Device submenu, create a simulator for it.
To add a simulator

Choose Hardware > Device > Manage Devices.
Xcode opens the Devices window.
At the bottom of the left column, click the Add button (+).
In the dialog that appears, enter a name in the Simulator Name text field and choose the device from the Device Type pop-up menu.
Choose the OS version from the iOS Version pop-up menu.
Alternatively, if the iOS version you want to use isn’t in the iOS Version pop-up menu, choose “Download more simulators” and follow the steps to download a simulator.
Click Create.
If the OS version you want to use is not installed, download it and follow the steps to add a simulator again.
To download a simulator
In Xcode, choose Xcode > Preferences.
In the Preferences window, click Downloads.
In Components, find the legacy simulator version you want to add, and click the Install button.
You can also delete and rename simulators in the Devices window.

To delete a simulator
In Simulator, choose Hardware > Device > Manage Devices, or in Xcode, choose Window > Devices.
Xcode opens the Devices window.
In the left column, select the simulator.
At the bottom of the left column, click the Action button (the gear next to the Add button).
Choose Delete from the Action menu.
In the dialog that appears, click Delete.
To rename a simulator, choose Rename from the Action menu and enter a new name.
For how to manage real devices that appear in the Devices window, read Devices Window Help.
Alter the Settings of the Simulated Device
You can alter the settings within Simulator to help test your app.
On a simulated device, use the Settings app. To open the Settings app, go to the Home screen and click or on tvOS, choose Settings. In Figure 1-8 you see the Settings app as it appears when launched in the iOS simulation environment.
The Simulator settings differ from the settings found on a hardware device. Simulator is designed for testing your apps, whereas a hardware device is designed for use. Because Simulator is designed for testing apps, its settings are naturally focused on testing, too. For example, in a simulated iOS device the Accessibility menu provides the ability to turn on the Accessibility Inspector, and the Accessibility menu on a device allows you to turn on and off different accessibility features.
Through the settings, you can test both accessibility and localization of your app. See Testing and Debugging in iOS Simulator for information on how to manipulate your settings for the various types of testing you are interested in.
Remember: Changes made in the Settings app of simulated device affect only the simulation environment that is currently running.
Rotate iOS Devices
You can use Simulator to manipulate the simulated device much as you do a physical device.
To rotate your simulated device, choose Hardware > Rotate Left. When you rotate your simulated device, Settings rotates (see Figure 1-9), just as it would on a hardware device.
Test in Simulator and on a Device
Simulator is designed to assist you in designing, rapidly prototyping, and testing your app, but it should never serve as your sole platform for testing. One reason is that not all apps are available in the simulator. For example, the Camera app is available only on hardware devices and cannot be replicated in the simulator.
In addition, not all bugs and performance problems can be caught through testing in Simulator alone. You’ll learn more about performance differences in Testing and Debugging in iOS Simulator. You can also find more information on testing your app on a device in Launching Your App on Devices in App Distribution Guide.
Quit Simulator
Simulator continues running until you quit it. Quitting Xcode will not close Simulator because they are separate applications. Similarly quitting simulator will not close Xcode.
To quit Simulator, choose Simulator > Quit Simulator. The device is shut down, terminating any running apps.
Note: Both Simulator and watchOS Simulator can be open at the same time.
Emulate Ios App On Mac Free
Mac Os Emulator For Windows
Iphone Simulator Mac
Iphone Emulator For Macbook
Mac Os Emulator Download
Can You Emulate On Ios
Copyright © 2018 Apple Inc. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Policy Updated: 2018-02-15